In this tutorial, we will study what is loop statements in c, why are they used, what are the types of loop statements, and how it works? So let us start.
What are the loops statements in c?
Loop statements in any language are used to execute a piece of the code number of times. By using the loop statements time of the programmer is saved. For example, if we want to execute a code 100 times we can use loops.
What are the types of the loop?
We have four types of loop statements: while loop, for loop, do-while loop, and nested loop. We will study each of them in detail.
While loop
In this, the condition is tested before executing the statement or group of statements. The execution of statements is done as long as the condition is true. The structure of the while loop is:
While (condition)
{
Statements;
}
Steps that are involved in the while loop are:
- Variable initialization
- Condition verification
- Variable increment or decrement
For loop
In this, the sequence of statements is executed after checking the condition. The structure of for loop is:
For( initial value; condition; increment or decrement )
{
The sequence of statements;
}
Steps that are involved in the for loop are:
- Evaluates the initialization code
- Check the condition
- If the condition is satisfied, the for loop is executed
- Increment/decrement condition is evaluated and again condition is checked
- Exit the loop, if the condition is not satisfied.
Do while loop
It is similar to the while loop but in this, the condition is checked at the end of the loop body. The structure of the do-while loop is:
Do {
Statements;
}while(condition);
Steps that are involved in the do-while loop are:
- First, the body of the loop is executed
- Then the condition is checked using while statements
- Exit the loop, If the condition is not satisfied.
Nested loop
In the case of nested loops, there are loops inside the loop. There are many types of nested loops like nested for loop, nested if-else loop, and so on. Following is an example of an if-else nested loop:
if(condition)
{ if(condition)
{
Statements;
}
else
{
Statements;
}
}
Else
{if(condition)
{
Statements;
}
Else(condition)
{
Statements;
}
Else if
{
Statements;
}
}
How does the loop work?
In the loop, if the condition is true then the statements inside the loop are executed. But if the condition is false, then the execution stops, and the loop is broken. After successful execution of the loop, the execution is started again from the loop entry and the condition is checked again and this process is repeated again and again.
The loop body is the sequence of statements that are kept inside curly braces. After the execution of statements, the condition is checked again, and if it is found to be true then the loop body is again executed. But if the condition is false, then the loop body is not executed and the execution is broken.
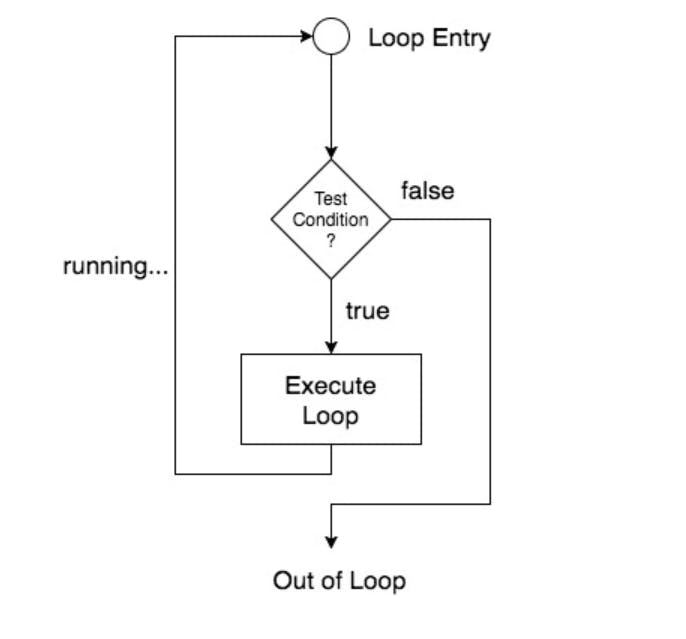
How to jump out of the loop?
To jump out of the loop there are two ways. One is by using break statements and the other is by using a continue statement.
- Break statement - As soon as the break statement is encountered the loop is immediately exited. The program continues from the statement which is right below the loop.
- Continue statement - By using this the control goes directly to the condition and the loop process continues. On encountering the continued statement, the cursor leaves the current cycle of the loop and the next cycle is continued.
Original Post - Loop statement

Post a Comment